The deposition of nutrients (namely, nitrogen and sulfur) in acidifying forms may cause changes in soil chemistry and subsequent acidification of the soil. Here, we assess the environmental impact of nitrogen oxides (NOx), ammonia (NH3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Cause-effect pathway
We propose a method to assess the acidification impact on vascular plant species, which are caused by the emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), ammonia (NH3), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
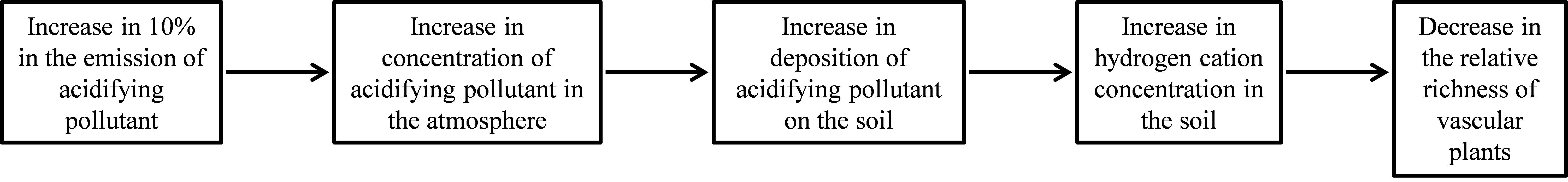
Modeling approach
The model consists of two parts. The fate factor models the atmospheric transport of the emitted pollutants and their subsequent impact on soil pH, while the effect factor models the sensitivity of the receiving ecosystem to soil acidity. The effect factor is based on the decline in richness of vascular plants.

